Hey there! Welcome to Statssy! Today we will learn how to calculate and interpret descriptive statistics in R.
Let us consider the daily sales of mangoes from your nearby shop for 28 days. Sometimes the sales are high, and sometimes the sales are low. But to understand the shop’s mango sales performance, we need to summarize the data. descriptive statistics in R
Table of Contents
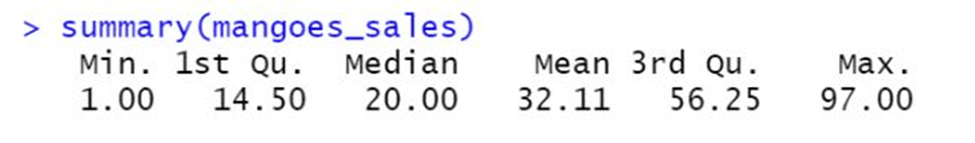
#daily sales written in R mangoes_sales <- c (20 , 56, 58, 9, 10, 59, 6, 15, 17, 50, 16, 18, 95, 20,15,13,17,58,10,25,26,57,1,59,28,97,34,10) #summarize the data summary(mangoes)
Explicit Interpretation
Now let us interpret each of the results one by one.
- Min. -> It represents the minimum value in the dataset. Here it is 1.0, which means the least shopkeeper sold in a day is 1.0 mango.
- 1st Qu. -> It represents the 25th percentile or first quartile of the dataset. Here it is 14.5, meaning 25% of the day the shopkeeper sold less than 14.5 mangoes, and 75% of days she sold more than 14.5.
- Median -> It represents the middle most value of the dataset. Here it is 20, meaning 50% of the days, the shopkeeper sold more than 20 mangoes, and for the rest, 50%, she sold less than 20 mangoes.
- Mean -> It represents the average number of mangoes sold. The average number means dividing total sales by the total number of days.
- 3rd Qu. -> It represents the 75th percentile or third quartile of the dataset. Here it is 56.25, which means on 25% of the days, the shopkeeper sold more than 56.25 mangoes, and on 75% of the days, the sales were less than 56.25 mangoes.
- Max -> It presents the maximum value in the dataset. Here it is 97, meaning the maximum shopkeeper sold in a day is 97.descriptive statistics in R
Implicit Interpretation
Now since we have interpreted what is directly available, there are some things that we can imply from these results.
For example, consider 25th and 75th percentile. We interpret each of them now if we see the difference between the two,
75th – 25th percentile = 56.25 – 14.50 = 41.75
This 41.75 value obtained by subtracting the 75th and 25th percentile is called IQR or Inter-quartile range. Why?
Because it represents the values between two quartiles, i.e., the first and third quartiles. Now, what does this means?
It shows where the middle 50% of the data values lie. In this case, we can say that on 50% of the days, the shopkeeper sold mangoes between 14.50 and 56.25.
Further Quests: Level Up Your Data Game
Ready to take your data game to the next level? Here’s a treasure trove of resources that are as binge-worthy as the latest Netflix series.
Books & Articles : descriptive statistics in R
Statistics Fundamentals
- Forecast Like a Pro with Exponential Smoothing in Excel
- Mean vs Median: The Ultimate Showdown
- Simple Linear Regression and Residuals: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Essential Data Terminology for Business Analytics
- Different Types of Statistical Analysis Techniques
- Understanding Residuals in Statistics
- Empirical Rule Calculator in Statistics
- Understanding Skewed Distributions
- Levels of Measurement in Statistics
- Understanding Z-Score in Business Statistics
- What is Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient
- How to Do Dsum Excel Function with And Criteria
R Programming
- Simple Linear Regression in R: A Super Chill Guide
- Mastering the Use of Letters in R Programming
- How to Calculate Coefficient of Variation in R Language
- How to Create and Interpret the Boxplot in R
- How to Create and Interpret Histogram in R Studio
Python Programming
- Your First Project in Data Analysis Using Python
- How to Create Boxplot in Python
- How to Create and Interpret Histogram in Python
- How to Calculate Coefficient of Variation in Python
- How to Use ‘With’ Keyword to Open Text File in Python
- Python XOR: Comprehensive Guide to Exclusive OR Operator
So, are you ready to embark on your next data quest?